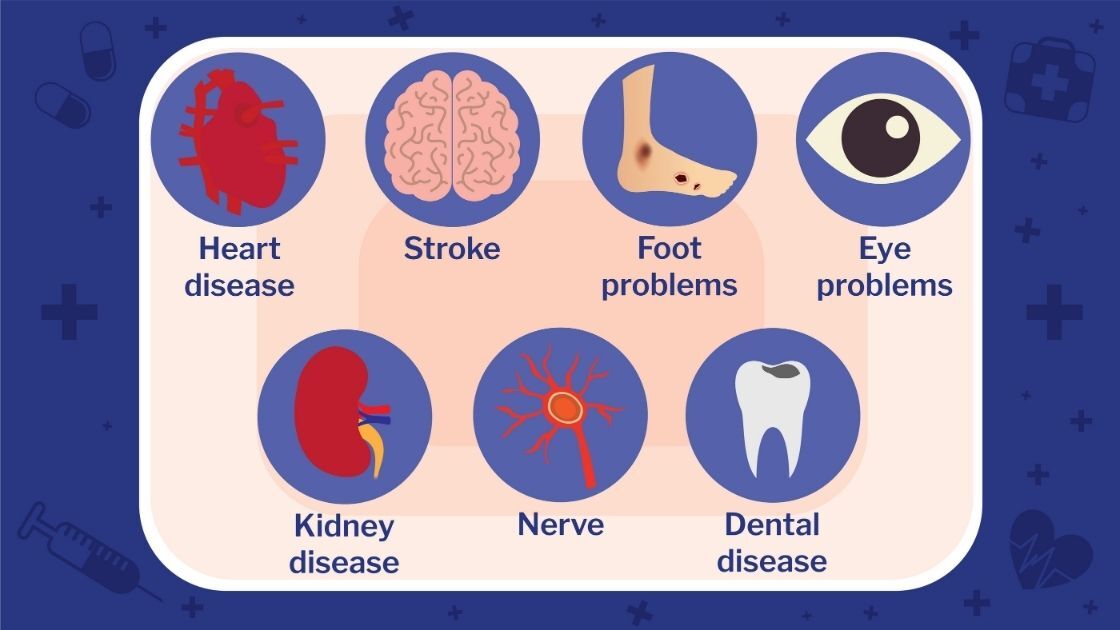
According to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), diabetes is a disease with high blood sugar levels. There are two types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. Type 1 diabetes is when the body does not produce insulin, usually diagnosed in children or young adults. Type 2 diabetes is when the body does not produce enough insulin or the insulin that is produced does not work properly. It is usually diagnosed in adults over the age of 40. Diabetes can lead to serious health complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, blindness, and amputation.
Whether you have recently received a diagnosis, have been battling type 1 or type 2 diabetes for some time, or are supporting a loved one, you have come to the right spot. With all the tools, health advice, and meal suggestions you require, this is the beginning of developing a deeper understanding of how you may lead a healthier life. Whatever stage your diabetes is in, remember that you have options and don’t have to be restricted. You can still have a fulfilling life. All you need to do is get started and keep going.
Here is what you can do to manage diabetes.
1. Say Yes To Fiber-Rich Foods
People with diabetes may be able to lower blood glucose levels over 12 weeks or less by increasing the amount of fiber in their diet. Most people, whether they have diabetes or not, don’t consume the daily allowance of 21 to 38 g of fiber. According to the American Diabetes Association, diabetics should strive for 14 g of fiber for every 1,000 calories they take daily. When possible, go for fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and sugar-free treats over refined-grain products like bread, rolls, and other baked goods.
2. Have Well-Balanced Meals
Plan each meal to include a healthy balance of carbs, fruits and vegetables, proteins, and fats. Be mindful of the kinds of carbohydrates you select. Certain sources of carbs, such as those found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, are healthier than others. These meals provide fiber to help keep your blood sugar levels steady and are low in carbohydrates. Discuss the best dietary options and the ideal balance of food kinds with your doctor or nutritionist.
3. Stay Hydrated
While exercising, drink plenty of water or other fluids because dehydration might impact blood sugar levels.
4. Exercise
People with diabetes can reduce their A1C by an average of 0.3 to 0.6 percentage points by beginning a regular exercise regimen. Doing 30 minutes of cardiovascular exercises, such as walking, using an exercise bike, or swimming at least five days a week is advisable. You can gain muscle by including two to three light strength-training sessions per week, which use blood sugar as fuel. In well-known research of 251 people with diabetes, those who engaged in aerobic and strength training three times per week for over six months observed a decrease in their A1C of almost 1%, a drop significant enough to reduce the risk of diabetes-related microvascular problems by a significant 35%.
5. Prevent Stress
Your blood sugar may rise if you’re under stress because of the hormones your body creates in reaction to ongoing stress. Furthermore, if you’re under a lot of additional stress, strictly adhering to your regular diabetes care routine could be more difficult.
6. Be Mindful Of Your Medication
When diet and exercise alone are insufficient for treating your diabetes, insulin and other diabetes drugs are intended to lower your blood sugar levels. However, when and how many of these medications are taken will determine their efficacy. Your blood sugar levels may be impacted by medicines you take for illnesses other than diabetes. It is advisable to consult your doctor to get the doses and the timings right.
7. Quit Smoking
Nearly one in every six diabetics are smokers. According to a study released by the CDC, smoking also increases your risk of developing heart disease, stroke, difficulty controlling your blood sugar, vision loss, nerve damage, kidney issues, and even amputation. Make another attempt to quit if you’ve already attempted. Combining counseling or a support group with nicotine replacement therapies and medications may be beneficial in reducing cravings.
8. Prevent Alcohol Consumption
Diabetes issues like nerve damage and eye degeneration might be made worse by alcohol. However, if your diabetes is under control and your doctor approves, an occasional alcoholic beverage is acceptable. Always consult your doctor before consuming alcohol.
9. Monitor Your Blood Sugar At Home
As often as your doctor advises, check your blood sugar levels. Testing your blood sugar at home can help you and your doctor better understands how well your medications are functioning, any potential side effects or other concerns, and how your food and exercise routines affect your blood sugar levels. Consult your doctor to determine what’s best for you.
10. Get Adequate Sleep
Try to sleep for 7 to 8 hours per night. Your mood and energy levels might be enhanced by getting enough sleep. If you feel sleepy often during the daytime, you may have obstructive sleep apnea, which is very common in those with diabetes. Speak to a healthcare professional if you have a sleep problem and diabetes.
To Sum It Up
There are various strategies to control your blood sugar levels naturally. Many involve lifestyle modifications, such as managing your weight, stress levels, sleep quality, exercising, and being hydrated. Having said that, your dietary decisions have a role in some of the most significant changes. Before adopting any lifestyle changes or experimenting with new supplements, make sure to see your healthcare provider, especially if you struggle to control your blood sugar or are currently taking medication.
And at DocVita, we can help you get in touch with the best healthcare professionals. All you need to do is visit our website and schedule your first session today.